Quick Summary: SMART objectives and goals provide the structure leaders need to translate strategy into measurable, aligned action. Their true value increases exponentially when paired with predictive intelligence, which surfaces risk, capacity strain, and alignment gaps long before they jeopardize delivery. For CIOs, PMO leaders, and technology executives, SMART objectives and goals are no longer administrative exercises—they are the foundation for foresight, accountability, and confident decision-making across complex portfolios.
Where Do SMART Objectives and Goals Struggle in Modern Project Environments
SMART objectives and goals have evolved from a performance-management framework into a strategic operating mechanism for modern organizations. As delivery cycles shorten, dependencies grow more complex, and teams stretch across time zones, leaders need a shared, unambiguous way to define success. SMART provides that anchor.
According to McKinsey, organizations with clearly stated goals outperform others on execution speed by removing decision friction and reducing cross-functional ambiguity. But even strong goals can fail in environments where conditions shift daily—capacity changes, risk surfaces mid-sprint, or new constraints emerge.
This is where predictive intelligence strengthens the discipline. SMART objectives and goals establish what must be achieved; predictive intelligence shows whether the current path will achieve it.
When integrated into delivery workflows, predictive intelligence adds:
- Early detection of goal drift
- Visibility into risks that SMART alone cannot see
- Forward-looking capacity insights
- Quality-trend signals tied to timelines
- Data-supported adjustments before slippage compounds
The combination transforms SMART objectives and goals from static statements into living, evidence-based commitments.
When your strategic objectives depend on early foresight—not late reporting—predictive visibility becomes non-negotiable. See how predictive signals strengthen SMART execution. Book a TrueProject demo.
What SMART Objectives and Goals Are—and What They’re Not
What exactly defines SMART objectives and goals?
SMART objectives and goals adhere to five key principles: specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time bound. In practice, they force teams to articulate outcomes with precision, not intention. For example: “Reduce project cycle time by 12% by Q4 through automated handoffs and improved resource allocation” is far more actionable than “Improve delivery speed.”

SMART removes interpretive ambiguity and creates a shared reference point for prioritizing, tracking, and evaluating performance across functions and workstreams.
How are SMART objectives and goals different from OKRs?
Although often grouped together, SMART and OKRs serve different purposes:
- OKRs stretch
- SMART operationalizes
OKRs drive ambition and directional alignment. SMART sharpens feasibility, measurement, and execution discipline. Together, they unify strategy with delivery accountability.
Why do SMART objectives and goals fail inside large organizations?
SMART fails not because the framework is flawed, but because organizations misuse or misunderstand it. The most common failure patterns include:
- Writing tasks instead of true outcomes
- Prioritizing outputs instead of impact
- Misalignment between team-level goals and enterprise priorities
- Goals that ignore real constraints—capacity, quality thresholds, dependencies, risk posture
- Goals that remain static even when conditions shift
SMART creates clarity—but clarity alone does not guarantee success when the environment is dynamic.
Where does predictive intelligence elevate SMART objectives and goals?
Predictive systems fill the execution blind spots that SMART alone cannot address. They diagnose performance trends and surface feasibility issues long before they escalate by revealing:
- Resource saturation that undermines whether an objective is achievable
- Risk accumulation that challenges whether it is realistic
- Quality drift that reshapes how it will be measured
- Dependency friction that threatens the time-bound element
- Conflicting assumptions that weaken its relevance
When SMART is supported by predictive signals, teams stop managing through optimism and begin managing through evidence.
If your objectives appear achievable but your execution data is telling a different story, you deserve an early signal—not a late surprise. Try the TrueProject SnapShot for a rapid, predictive assessment.
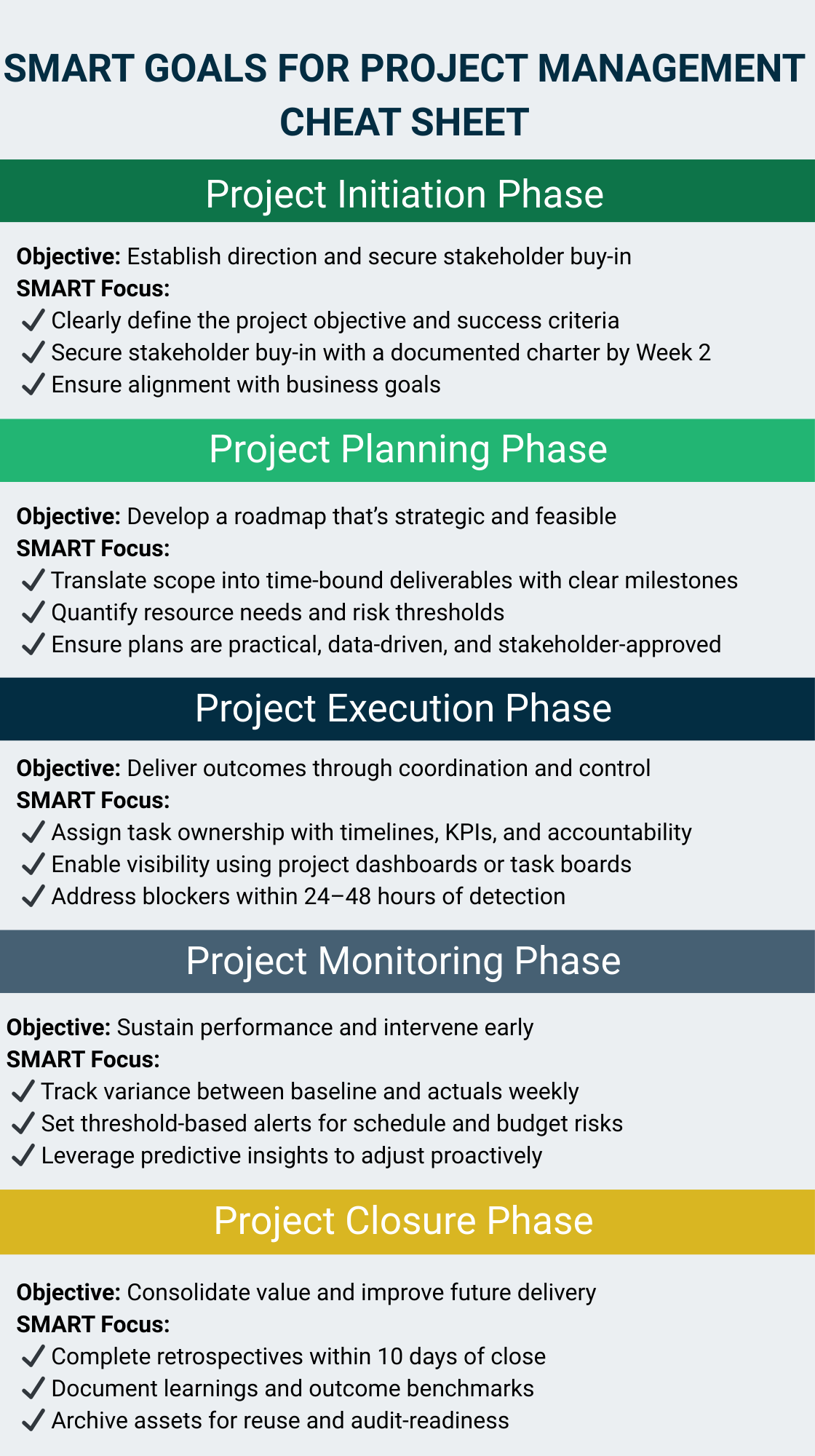
How SMART Objectives and Goals Strengthen Project Delivery
SMART objectives and goals are the structural backbone of predictable execution. They help delivery organizations translate strategy into concrete, measurable actions while reducing ambiguity—a key reason many large initiatives stall. PMI notes that only 48% of projects deliver on their original goals, largely due to vague scoping or shifting expectations. SMART mitigates this by creating clarity before work begins.
But clarity alone isn’t enough. The velocity and complexity of enterprise projects mean leaders must also understand whether each SMART objective is genuinely feasible under real conditions—capacity constraints, dependencies, cycle-time trends, integration pressures, or quality thresholds. This is where SMART and predictive advanced technology solutions intersect.
How do SMART objectives and goals strengthen project governance?
SMART elevates governance by requiring teams to establish:
- Explicit commitments (“What exactly are we delivering?”)
- Real metrics (“How will we measure it?”)
- Feasibility checks (“Do we have the capacity?”)
- Business alignment (“Why does this objective matter?”)
- Time-bound certainty (“When must it be done?”)
Governance moves from subjective interpretation to measurable accountability.
How do SMART objectives and goals support large, cross-functional initiatives?
Enterprise programs often span product, engineering, security, operations, finance, and vendors—all with distinct definitions of “done.” SMART reduces misunderstandings by creating:
- Shared definitions
- Consistent progress formats
- Unified metrics
- A single source of truth for success
This creates orchestration rather than fragmentation.
How does predictive intelligence elevate project-level SMART objectives?
SMART defines clarity.
Predictive intelligence defines confidence.
Predictive signals proactively reveal:
- Emerging risk patterns
- Defect acceleration in critical phases
- Overloaded roles (≥85–90% utilization)
- Timeline threats from upstream slippage
- Dependencies trending toward conflict
- Quality gates drifting from threshold
Leaders no longer wait for mid-cycle surprises; they adjust early.
 If your SMART objectives depend on real-time clarity across teams, early foresight becomes a competitive advantage. See where your objectives stand now with a TrueProject QuickStart review.
If your SMART objectives depend on real-time clarity across teams, early foresight becomes a competitive advantage. See where your objectives stand now with a TrueProject QuickStart review.
How SMART Objectives and Goals Align Teams and Drive Accountability
Alignment is the multiplier of execution speed. Even strong teams underperform when their goals diverge, contradict, or lack visibility. SMART objectives and goals resolve this by giving everyone—from executive sponsors to delivery squads—a common vocabulary for priorities, outcomes, and commitments.
How do SMART objectives and goals create alignment at scale?
SMART supports enterprise-wide synchronization by:
- Making priorities visible to everyone
- Reducing interpretation gaps
- Linking individual and team goals to organizational strategy
- Eliminating contradictions across programs
- Keeping teams focused even as conditions change
Alignment is not a communication exercise—it is a structural one. SMART provides that structure.
How do SMART objectives and goals reinforce accountability?
Accountability is strongest when expectations are explicit, measurable, and trackable.
SMART provides:
- Clear ownership
- Outcome-based expectations
- Timelines tied to real workload
- Success metrics visible to sponsors and teams
Predictive intelligence strengthens accountability by exposing early performance drift:
- Delayed handoffs
- Capacity spikes
- Quality drop-offs
- Lagging decision cycles
- Emerging misalignment across functions
SMART says what is expected. Predictive intelligence shows what’s happening beneath the surface.
By embedding SMART within execution tools—not separate documents—alignment endures even as teams scale.

How SMART Objectives and Goals Reinforce Performance, Growth, and Results
SMART objectives and goals are not just project tools—they reinforce performance across all layers of the organization. When integrated across HR, CRM, sales, delivery, and leadership systems, SMART creates consistency in how progress is measured and how expectations are set.
How do performance management systems incorporate SMART objectives and goals?
Enterprise talent platforms embed SMART frameworks into:
- Quarterly performance cycles
- Leadership competency assessments
- Skill development plans
- Project-based evaluations
This encourages measurable contribution rather than effort-based evaluation.
Predictive intelligence ensures that performance assessments account for systemic constraints—not just individual effort—by identifying:
- Structural blockers
- Cross-team delays
- Overloaded roles
- Quality issues created upstream
- Dependency-driven delays
This leads to more fair, accurate, and future-ready performance conversations.
How do CRM systems use SMART objectives to drive revenue outcomes?
CRM platforms translate SMART into sales performance by defining:
- Precise pipeline growth targets
- Conversion-rate expectations
- Account retention goals
- Quarterly revenue milestones
Predictive intelligence then forecasts:
- Deal slippage probability
- Conversion likelihood
- Account health
- Time-to-close trends
This transforms SMART goals into predictive revenue insights. SMART brings clarity. Predictive intelligence brings direction.
When personal, team, and organizational goals align, execution becomes significantly more predictable. Explore how predictive insights strengthen cross-level alignment. Schedule a discussion.
How SMART Objectives and Goals Improve Measurement, Forecasting, and Performance Evaluation
Measurement is where SMART objectives and goals shift from strategy to operational truth. Leaders care not only about setting clear objectives but also about assessing progress accurately and identifying issues early. SMART provides the scoring model; predictive intelligence provides the early-warning system.
How do SMART objectives and goals strengthen measurement accuracy?
SMART improves measurement by defining:
- Specific metrics that reduce interpretive errors
- Operational thresholds for quality, speed, or budget
- Clear baselines for evaluating delta changes
- Scannable targets that keep teams oriented
But classic SMART measurement is backward-looking—it evaluates after the fact.
Predictive intelligence shifts measurement forward, enabling leaders to:
- Forecast whether SMART targets will be met
- Detect negative delivery patterns early
- Quantify risk buildup against SMART thresholds
- Identify capacity constraints before timelines slip
- Compare predicted vs. actual performance with MAPE or similar metrics
This helps executives intervene while adjustments are still cost-effective.
How do SMART objectives and goals influence portfolio reviews?
Portfolio governance improves when SMART becomes the foundation for review cycles:
- Red, amber, and green statuses become data-backed—not opinion-based.
- Cross-team alignment issues surface earlier.
- Performance variation across teams becomes identifiable.
- Objectives translate directly into delivery dashboards.
- Sponsors gain confidence because goals have measurable commitment.
Predictive intelligence strengthens these reviews further with:
- Probability of goal completion
- Risk-adjusted estimates
- Impact of emerging constraints
- Forecasted quality and delivery variance
Executives don’t just see where things stand—they see where they are heading.
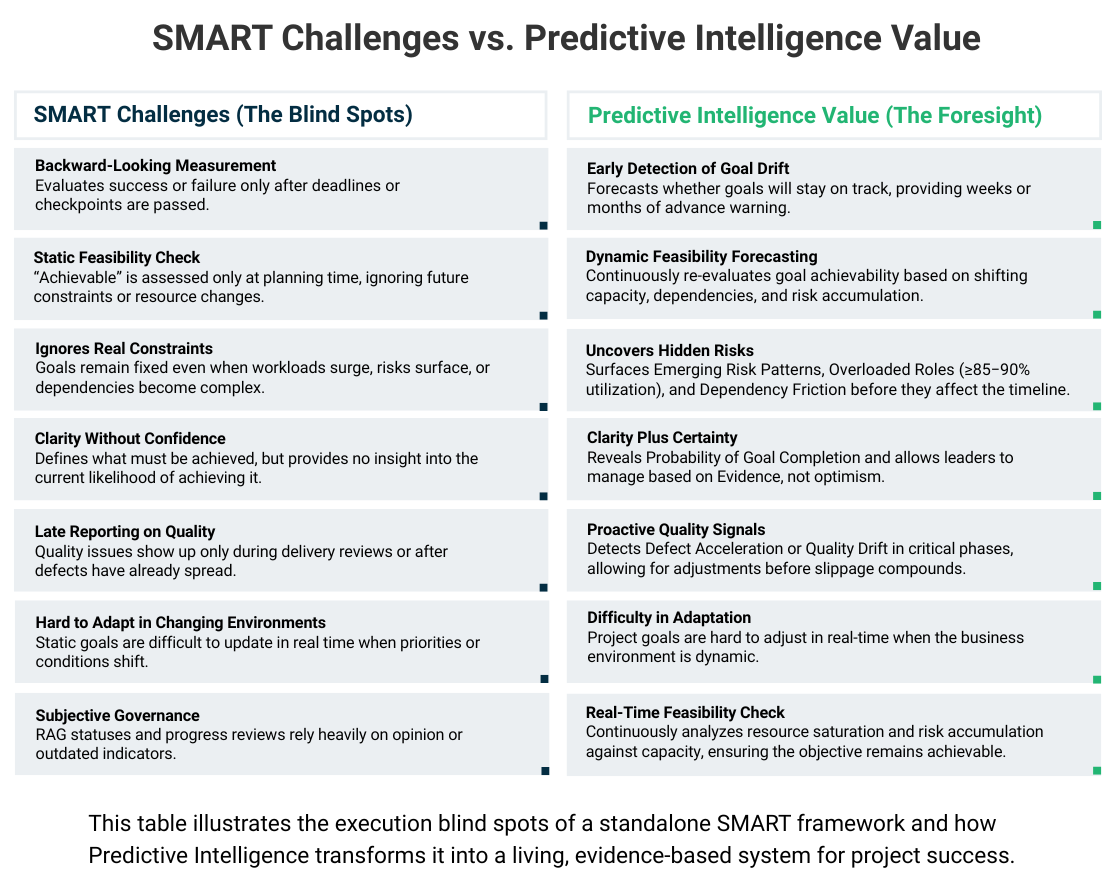
What Are the Hidden Challenges of SMART Objectives and Goals (and How Predictive Intelligence Solves Them)
How does predictive intelligence solve these issues?
Predictive intelligence fills in SMART’s blind spots by:
- Identifying whether the “achievable” component is realistic under real capacity
- Uncovering dependency conflicts across teams
- Surfacing early quality and timeline risk through leading indicators
- Tracking alignment drift between objectives and delivery actions
- Predicting slippage before it affects business outcomes
SMART creates clarity. Predictive intelligence creates certainty.
Can SMART objectives and goals adapt in real time?
With predictive data, yes.
SMART objectives and goals become dynamic:
- Adjusting targets based on evolving risks
- Refining expectations as constraints shift
- Strengthening timelines based on quality patterns
- Realigning teams based on updated probability of success
This moves SMART from a quarterly ritual to an active operational discipline.
SMART Goals vs Predictive Intelligence: Real-World Lessons
1. When SMART Goals Fail: CrowdStrike Falcon Update Outage
What Happened:
In July 2024, CrowdStrike’s Falcon security software update caused the largest IT outage in history, crashing 8.5 million systems, disrupting 7,000 flights, and affecting 1.3 million customers globally.
Why It Failed - SMART goals for deployment focused on speed and completion but lacked predictive risk analysis. No proactive checks were in place to forecast cascading failures in complex IT ecosystems.
Impact - Estimated global losses exceeded $5 billion.
Lesson - SMART goals without predictive intelligence can lead to catastrophic failures in dynamic environments like software updates. Predictive analytics could have flagged anomalies before rollout. (Brilworks)
2. When Predictive Intelligence Wins: Walmart’s AI-Powered Forecasting
What Happened - Walmart leveraged AI-driven predictive analytics to optimize inventory and forecast demand, reducing stockouts and overstock issues.
Contrast to SMART Failure - Traditional SMART goals in retail often focus on “reduce stockouts by X% in Y months,” but without predictive foresight, these goals fail when demand fluctuates unexpectedly.
Impact - Predictive intelligence enabled Walmart to anticipate demand shifts, improve customer satisfaction, and cut operational costs significantly.
Lesson - Predictive analytics transforms SMART goals from static targets into dynamic, data-driven strategies that adapt to real-world changes. (SuperAGI)
The Future of SMART Objectives and Goals: Precision, Predictive Insight, and Real-Time Alignment
SMART objectives and goals were built for clarity. The next era demands clarity plus foresight. Modern PMOs are shifting toward intelligent goal systems that learn from execution data, detect alignment friction, and recommend adjustments before performance drifts.
What future trends will redefine SMART objectives and goals?
1. AI-powered objective calibration
Systems will recommend wording, metrics, and thresholds based on:
- historical patterns
- team capacity
- risk trends
- program complexity
- typical delivery variation
Instead of writing SMART goals manually, leaders will validate intelligently generated drafts.
2. Dynamic SMART objectives refreshed through predictive models
Goals will evolve in real time as conditions change—capacity shifts, dependency conflicts, supply-chain issues, or quality concerns.
3. Alignment intelligence
Systems will highlight where goals across teams contradict, drift, or compete for the same constrained resources.
4. Intelligent scenario planning
SMART objectives will link to scenario simulations that test:
- feasibility
- risk exposure
- effort distribution
- time-to-completion
- resource shifts
5. “Outcome quality scoring” for goals
Beyond evaluating whether goals were met, organizations will track:
- efficiency of delivery
- cost to achieve the outcome
- risk avoided
- quality maintained
Predictive intelligence will anchor all of it.
How should CIOs and PMO leaders prepare for the next generation of SMART?
They should invest in the foundational elements:
- Execution telemetry (task cycles, quality, capacity, dependencies)
- Predictive analytics that detect early drift
- Unified collaboration platforms where SMART lives in the workflow
- Cross-team alignment structures (shared definitions, shared KPIs)
- A governance model that rewards evidence-based adjustments
SMART will increasingly become an ecosystem—not a template.
How Predictive Intelligence Reinforces SMART Objectives and Goals Across the Project Lifecycle
SMART objectives and goals define what needs to happen. Predictive intelligence reveals whether it will happen—and how early teams must intervene to protect outcomes. This integration shifts leaders from reactive oversight to proactive governance.
How does predictive intelligence protect SMART commitments?
Predictive intelligence strengthens SMART execution by continuously analyzing:
- Project velocity
- Dependency friction
- Quality stability
- Decision latency
- Resource pressure
- Stakeholder alignment
These signals uncover risks weeks or months before they appear in traditional status reviews. Leaders gain foresight into whether SMART targets remain achievable under changing delivery conditions.
How does predictive intelligence improve alignment and feasibility?
Predictive models evaluate whether objectives are realistically achievable by:
- Forecasting workload vs. capacity
- Highlighting teams at risk of overload
- Predicting timeline slippage
- Detecting objective drift
- Stress-testing dependencies
- Surfacing conflicting assumptions
This creates a real-time feasibility check for every SMART objective in a portfolio.
How does predictive intelligence support adaptive SMART planning?
Adaptive SMART planning is where objectives evolve based on evidence—not guesswork.
Predictive systems enable leaders to:
- Recalibrate SMART goals based on emerging constraints
- Strengthen timelines using real delivery data
- Update measurable targets using performance patterns
- Redirect teams before slippage compounds
- Replace outdated assumptions with live forecasts
SMART becomes not just structured—but self-correcting.
Conclusion — SMART Objectives and Goals That Deliver Real Results
SMART objectives and goals work only when they create clarity, strengthen alignment, and translate strategy into measurable action. Their value rises when they withstand shifting conditions, cross-team complexity, and delivery pressures. For leaders managing high-stakes programs, the advantage lies not just in defining success but in knowing—early and confidently—whether the organization is on track to achieve it.
But clarity without foresight isn’t enough. Predictive intelligence transforms SMART objectives and goals from static statements into living commitments—continuously monitored, stress-tested, and recalibrated using real execution data, stakeholder input, and risk patterns.
And this is where TrueProject becomes indispensable.
TrueProject is a SaaS-based Strategic Project Intelligence (SPI) solution powered by predictive AI that foresees project risks weeks or even months in advance. By continuously analyzing project data and stakeholder input against key performance indicators, it delivers clear, actionable insights—empowering leadership to act decisively from any dashboard before problems ever surface.
For organizations striving to make SMART objectives and goals truly SMART—accurate, achievable, evidence-based, and outcome-oriented—TrueProject provides the intelligence layer that keeps objectives realistic, aligned, and fully supported by real-time project health.
If your SMART goals demand proactive visibility across teams, risk, and delivery conditions, predictive intelligence gives you that confidence. Don’t wait for gaps to surface—see them ahead of time. Book a TrueProject demo.
FAQs
1) What are SMART objectives and goals in project management?
SMART objectives and goals are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound commitments that clarify what success looks like and how it will be evaluated.
2) Why are SMART objectives and goals important for modern delivery teams?
They reduce ambiguity, improve alignment, accelerate decisions, and create consistent expectations across cross-functional teams.
3) How do SMART objectives and goals differ from OKRs?
SMART focuses on execution and feasibility; OKRs emphasize ambition and directional alignment. Many organizations use SMART for delivery and OKRs for strategy.
4) How does predictive intelligence improve SMART goal performance?
It forecasts risk, identifies constraints early, and detects alignment drift—ensuring SMART goals remain achievable throughout execution.
5) Can SMART goals adjust over time?
Yes. With predictive insights, SMART goals adapt based on evolving constraints, workload shifts, and early risk indicators.
7) What makes predictive intelligence essential for SMART goal success?
It ensures leaders know beforehand whether goals remain achievable, helping organizations make informed adjustments proactively.






